Neodymium Rare Earth Magnet FAQ
- What is a Magnet?
- What are permanent magnets made of?
- How are magnets made?
- What does the "N rating" of the neodymium magnets mean?
- How permanent is a Neodymium magnet's strength?
- What might affect a magnet's strength?
- How does a magnet's strength drop off over distance?
- Can a magnet that has lost its magnetism be re-magnetized?
- Can I make a magnet that I already have any stronger?
- How do you measure the strength or power of a magnet?
- If I have a Neo magnet with a Br of 13,800 Gauss, should I be able to measure 13,800 Gauss on its surface?
- Why is the surface gauss so much lower than the manufacturers N-Rating?
- What are Magnetic Poles?
- How is North Pole Defined?
- What are the standard industry definitions of "North" and "South" Pole?
- Can I buy magnets with the North Poles already marked?
- How can you tell which is the North Pole if it is not marked?
- What are the different types of magnets available?
- What are Rare Earth Magnets?
- Which are the strongest permanent magnets?
- What does 'orientation direction' mean?
- What is the pull strength of your magnets?
- Can Neodymium (Nd-Fe-B) magnets be drilled and machined?
- Will Neodymium magnets demagnetize if I heat them?
- Do magnets pose a health risk?
- Can magnets cure disease?
- Do you sell single pole or monopole magnets?
- Where are the North and South poles on these magnets?
- Is it possible to become addicted to playing with magnets?
What is a Magnet?
A magnet is an object that has a magnetic field. The word magnet comes from the Greek "magnitis lithos", which means "Magnesian stone." Magnesia is an area in Greece where deposits of magnetite have been discovered since antiquity.
In the modern sense, a magnet is any material that has a magnetic field. It can be in the form of a permanent (or static) magnet or an electromagnet. Permanent magnets do not rely upon outside influences to generate their field. Electromagnets rely upon electric current to generate a magnetic field--when the current increases, so does the field.
What are permanent magnets made of?
Modern permanent magnets are made from special alloys to create increasingly better magnets. The most common families of magnet materials today are: Ferrites; Alnicos (Aluminum-Nickel-Cobalt); Ceramics; Samarium-Cobalts; and Neodymiums (Neodymium-Iron-Boron, NdFeB). Neodymiums and Samarium-Cobalts are collectively known as Rare Earths.
How are magnets made?
Modern magnet materials are made through casting, pressing and sintering, compression bonding, injection molding, extruding, or calendaring processes.
What does the "N rating" of the neodymium magnets mean?
The grade, or "N rating" of the magnet refers to the Maximum Energy Product of the material that the magnet is made from. It refers to the maximum strength that the material can be magnetized to. The grade of neodymium magnets is generally measured in units millions of Gauss Oersted (MGOe). A magnet of grade N48 has a Maximum Energy Product of 48 MGOe. Generally speaking, the higher the grade, the stronger the magnet.
How permanent is a Neodymium magnet's strength?
If a magnet is stored away from power lines, other magnets, high temperatures, and other factors that adversely affect the magnet, it will retain its magnetism essentially forever.
What might affect a magnet's strength?
The factors can affect a magnet's strength: heat; strong electrical currents in close proximity to the magnet; Neodymium magnets will corrode in high humidity environments unless they have a protective coating. Shock and vibration do not affect modern magnet materials, unless sufficiently strong to physically damage the material itself.
How does a magnet's strength drop off over distance?
The strength of a magnetic field drops off roughly exponentially over distance.
Can a magnet that has lost its magnetism be re-magnetized?
Provided that the material has not been damaged by extreme heat, the magnet can be re-magnetized back to its original strength.
Can I make a magnet that I already have any stronger?
Once a magnet is fully magnetized, it cannot be made any stronger - it is "saturated". In that sense, magnets are like buckets of water: once they are full, they can't get any "fuller".
How do you measure the strength or power of a magnet?
Most commonly, Gaussmeters, Magnetometers, or Pull-Testers are used to measure the strength of a magnet. Gaussmeters measure the strength in Gauss, Magnetometers measure in Gauss or arbitrary units (so its easy to compare one magnet to another), and Pull-Testers can measure pull in pounds, kilograms, or other force units. Special Gaussmeters can cost several thousands of dollars.
If I have a Neo magnet with a Br of 13,800 Gauss, should I be able to measure 13,800 Gauss on its surface?
No. The Br value is measured under closed circuit conditions. A closed circuit magnet is not of much use. In practice, you will measure a field that is less than 13,900 Gauss close to the surface of the magnet. The actual measurement will depend on whether the magnet has any steel attached to it, how far away from the surface you make the measurement, and the size of the magnet (assuming that the measurement is being made at room temperature). For example, a 1" diameter N-48 Neo magnet that is 1/4"long, will measure approximately 2,800 Gauss 1/16" away from the surface, and 2,466 Gauss 1/8" away from the surface.
Why is the surface gauss so much lower than the manufacturers N-Rating?
Quite often gauss magnetic strength is misquoted or exaggerated. One common misunderstanding is the difference between what is called the Manufacturer's Rating and the actual Surface Gauss Rating of a magnet,. The Manufacturer's Rating is much higher than the Surface Gauss, and represents two different ways of measuring the strength.
Manufacturer's Rating: Technically this is called the Magnetic Remanence (Br) of the magnetic material and is a property of the magnet when measured in the manufactures original magnetizing equipment, in what's called a closed circuit. It indicates the magnetic field strength remaining inside the magnet (or at its core) and represents a grade of magnetic material. This measurement is much higher than the surface gauss reading.
Surface Rating: The gauss rating is measured on the surface of the magnet and represents the magnetic flux density generated outside the magnet body. Strictly speaking this is the rating which is most useful to end users as this indicates the accessible gauss of the magnet.
Surface Gauss alone does not tell you the strength of a magnet. If you have two different sized magnets with the same Surface Gauss, the larger magnet will be stronger. Or, you could have a small magnet with a high Surface Gauss that will pull less than a larger magnet with a lower Surface Gauss.
What are Magnetic Poles?
Magnetic Poles are the surfaces from which the invisible lines of magnetic flux emanate and connect on return to the magnet.
All magnets have two poles, a North pole and a South pole. By convention, we say that the magnetic field lines leave the North end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. This is an example of a magnetic dipole ("di" means two, thus two poles). If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter how small the pieces of the magnet become, each piece will have a North pole and a South pole. It has not been shown to be possible to end up with a single North pole or a single South pole which is a monopole ("mono" means one or single, thus one pole).
Opposite poles attract each other (North attracts South), while like poles repel (North repels North, and South repels South).
The Earth has a magnetic field with a North pole and a South pole.
How is North Pole Defined?
There is much confusion around this issue mainly because there are different conventions or starting points about how to define a north pole. There is an engineering and scientific convention; but there is also a medical or magnetic therapy understanding.
Science: Defines a North pole as the end of the magnet which points to the Earth's geographical North Pole, in other words it is actually saying that the Earth's geographical North pole is a magnetic South pole. This is why, if you hold a compass up to a magnet, the needle will point to the South pole of the magnet. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
Magnetic Therapy: Bio North: The magnetic therapy starting point says that the Earths geographical North Pole is a magnetic north pole, therefore whatever points to the north pole i.e. the end of a compass needle, is a south pole (as opposites attract). This is the common sense approach, i.e. the Earths North Pole is a north pole. A north pole from this point of view is often called Bio North or Negative North. The end of the compass needle with the N or arrow will point to the Bio North pole.
What are the standard industry definitions of "North" and "South" Pole?
The North pole is defined as the pole of a magnet that, when free to rotate, seeks the North pole of the Earth. In other words, the North pole of a magnet seeks the North pole of the Earth. Similarly, the South pole of a magnet seeks the South pole of the Earth. (Again, keep in mind that the earth's physical North pole acts like the South pole of a magnet.)
Can I buy magnets with the North Poles already marked?
Yes, please see our line of pole indicated magnets.
How can you tell which is the North Pole if it is not marked?
You can't tell by looking. You can tell by placing a compass close to the magnet. The end of the needle that normally points toward the North pole of the Earth would point to the South pole of the magnet.
What are the different types of magnets available?
There are 2 types of magnets: permanent magnets and electro-magnets.
Permanent magnets emit a magnetic field without the need for any external source of power. Electro-magnets require electricity in order to behave as a magnet.
There are various different types of permanent magnet materials, each with their own unique characteristics. Each different material has a family of grades that have properties slightly different from each other, though based on the same composition.
What are Rare Earth Magnets?
Rare Earth magnets are magnets that are made out of the Rare Earth group of elements. The most common Rare Earth magnets are the Neodymium-Iron-Boron and Samarium Cobalt types.
Which are the strongest permanent magnets?
The most powerful permanent magnets available today are the Rare Earths. Of the Rare Earths, Neodymium-Iron-Boron types are the strongest. However, at elevated temperatures (of approximately 150 C and above), the Samarium Cobalt types can be stronger that the Neodymium-Iron-Boron types (depending on the magnetic circuit).
What does 'orientation direction' mean?
Most modern magnet materials have a "grain" in that they can be magnetized for maximum effect only through one direction. This is the "orientation direction", also known as the "easy axis", or "axis".
Unoriented magnets (also known as "Isotropic magnets") are much weaker than oriented magnets, and can be magnetized in any direction. Oriented magnets (also known as "Anisotropic magnets") are not the same in every direction - they have a preferred direction in which they should be magnetized.
What is the pull strength of your magnets?
Pull strength is a very subjective measure that is dependent upon many factors such as:
- Type of material being pulled against;
- Surface conditions;
- Physical contact;
- Magnet characteristics such as plating composition; and
- Presence or absence of lateral and rotational forces.
All that being said, a 1 inch diameter by 1/8 inch thick plated N48 disc magnet will lift about 12.2 lbs of ferrous steel under ideal conditions.
Can Neodymium (Nd-Fe-B) magnets be drilled and machined?
Not easily or safely. Neodymium sintered magnets behave like a ceramic. They have a tendency to crack and chip when drilled. Additionally, the powder produced when machining these magnets is flammable. Lastly, machining causes heat to build up in the magnet which may result in it being demagnetized. Most likely, a drilled or machined Neo magnet will be made unusable by the process due to breakage, cracking or heat damage.
Will Neodymium magnets demagnetize if I heat them?
Yes, if heated beyond 176 degrees Fahrenheit (80 degrees Celsius) the magnets will quickly loose their magnetic properties. Sustaining these temperatures for a length of time or heating the magnet significantly higher than this will permanently demagnetize it. Other types of magnets such as Samarium-Cobalt have higher heat resistance. There are also other types of Nd-Fe-B magnets that are not as susceptible to heat induced flux degradation.
Do magnets pose a health risk?
No, unless you have an internal medical device such as a pacemaker that would be affected by a strong magnetic field. However, Neodymium magnets are very strong and should be handled with care. These magnets can pinch if allowed to come together against the skin and larger magnets are capable of breaking bones. For this reason, children should not be allowed to play with the larger magnets.
Can magnets cure disease?
We have never seen definitive proof that magnetic therapy is effective. You should seek qualified medical assistance if you have a health problem.
Do you sell single pole or monopole magnets?
They do not exist. By definition, all magnets have two poles.
Where are the North and South poles on these magnets?
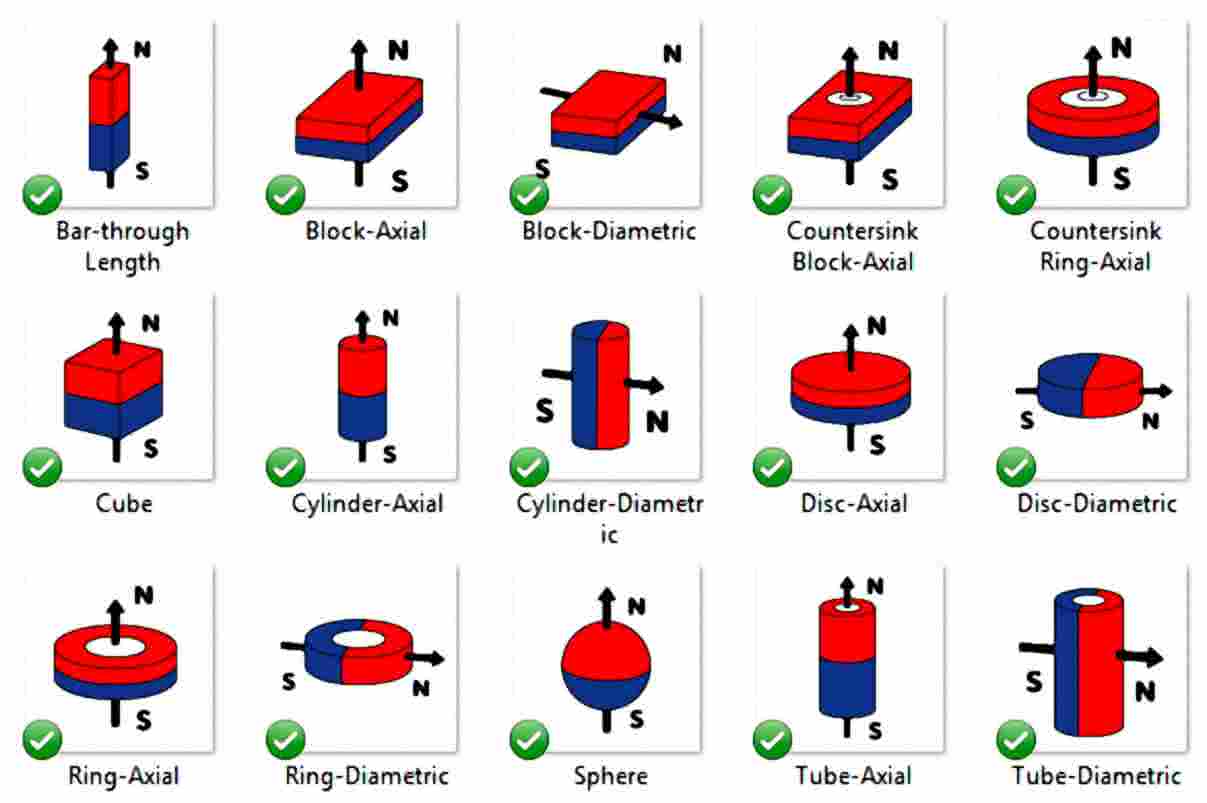
Is it possible to become addicted to playing with magnets?
Yes, that is why we are in business. We play with them every day!
